While no OSINT website can replace a solid framework and talented analysts, having the right tools at your disposal can certainly help you gather intelligence faster, better, and more efficiently.
You can find hundreds of open-source intelligence resources online – with prices ranging from free to very expensive. They can also serve many different functions throughout the intelligence cycle, from data collection and processing to analysis and dissemination. The resources available to OSINT investigators keep growing each year.
This growth is exciting! If you have a problem, there’s probably a tool out there that can help you solve it. But with all of these resources, how do you know which ones are worth trying?
This post will help clarify some of those decisions for you. Let’s check out some top OSINT websites and tools every analyst should keep handy in their bookmark folders.
Learn More: 5 Cognitive Biases That Could Affect Your OSINT Investigations
1. The Wayback Machine
Content published online is ephemeral.
For that reason, seasoned OSINT analysts always record any information uncovered through the course of an investigation. It might be deleted or removed the next time they visit the site.
But this isn’t an option for security teams looking to review sources in the past. Thankfully, that’s where the Wayback Machine can come in handy.
This digital archive service takes screenshots of websites on a regular basis. This allows investigators to see how a page looked at various points in time.
And since launching in 1996, it has cached over 625 billion web pages in addition to millions of videos, audio recordings, and software programs.
For researchers, this can reveal information that may no longer be available online or findable through regular search engines.
Say authorities seized a website so you can no longer access the original content. Or maybe a person of interest has deleted their social media posts and comments.
Despite these challenges, the Wayback Machine allows investigators to still uncover information that may have been removed from the web. 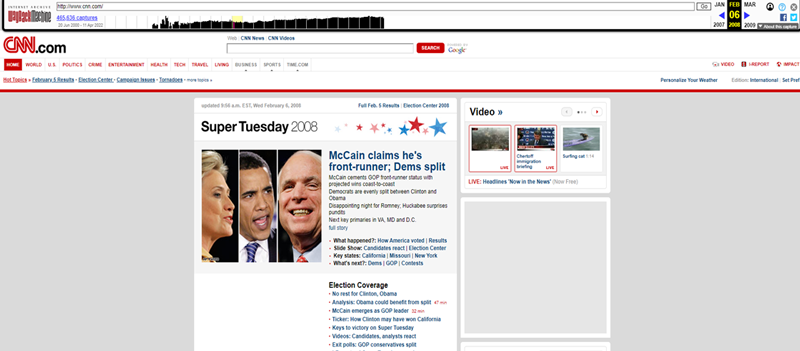 The homepage of CNN.com on February 6, 2008, captured by the Wayback Machine.
The homepage of CNN.com on February 6, 2008, captured by the Wayback Machine.
2. OSINT Framework
You can use any number of tactics and techniques to collect intelligence online.
But with information dispersed across the web, using different methods with each investigation becomes too time-consuming. That’s why most organizations and investigators employ a system with regard to information retrieval.
OSINT Frameworkprovides a template for this kind of system.
The site helps researchers find free, or low-cost, open-source resources. Users can browse through various OSINT tools based on the needs of their investigation.
For example, say you’re looking for tools to assist with geolocation. Click on the ‘Geolocation’ section, then OSINT Framework will return dozens of helpful resources.
Originally, the site first catered to professionals in the cybersecurity space. In recent years, however, OSINT Framework added tools and resources for other applications as well.
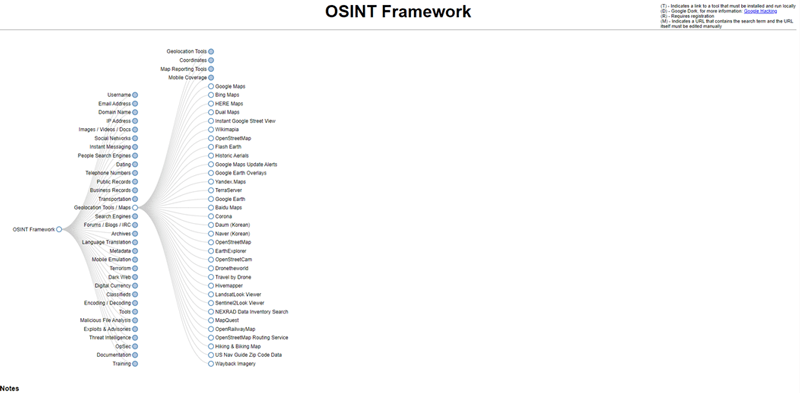
A collection of free OSINT tools for geolocation research, provided by OSINT Framework.
3. Social Searcher
Monitoring social media for potential threats represents a tedious process. It becomes even more time-consuming when you have to watch several different platforms on an ongoing basis.
Social Searcher represents a quick fix to this problem.
This search engine allows users to monitor mentions of key terms across social media. That enables OSINT analysts to quickly measure and track what people are saying about an executive, brand, or location in one place.
To be clear, tools designed for marketers, like Social Searcher, do have certain limitations.
For instance, the site only scans a handful of the largest, most popular platforms. As a result, analysts could overlook valuable intelligence on smaller, alt-tech sites.
Additionally, the free version of the site limits the number of query submissions per day.
That said, it does serve as a helpful resource to get started with social media threat monitoring.
 A screenshot of SocialSearcher.com
A screenshot of SocialSearcher.com
4. Distill.io
OSINT is all about creating actionable intelligence from open-source information. But combing through Google searches or constantly refreshing web pages can be time-consuming – especially if you have to monitor multiple targets.
Fortunately, Distill.io makes it easy to automate some of this process.
Distill.io is a mostly-free browser plugin. After installing the app, select the part of the page you want to track and set up the interval.
After that, Distill.io will automatically alert you whenever a website is updated.
This can have several OSINT applications for corporate security teams, such as gathering intelligence on competitors, monitoring a VIP’s online reputation, or tracking new SEC filings.
5. TinEye
Pictures make up the bulk of content on the web. For that reason, conducting a reverse image search often come in handy for OSINT research.
Canada-based TinEye is an image-focused web crawling database.
The application allows users to search by image and figure out where else it may have been published online. This can be done by uploading an image to TinEye or searching by URL.
This might be needed to identify a person of interest, determine the location where a photo was taken, or debunk online mis- and disinformation circulating online.
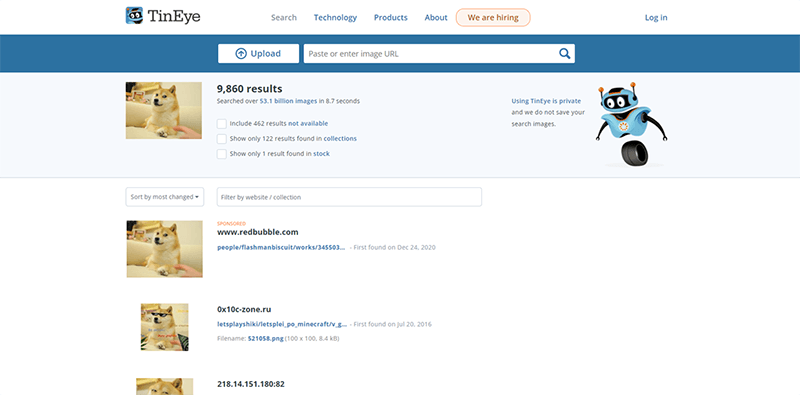 The results of a reverse image search, provided by TinEye.com
The results of a reverse image search, provided by TinEye.com
6. Intelligence X
While Google represents a powerful tool for open-source investigators, it has limitations.
Queries are limited to what Google decides to index. As a result, investigators that become too reliant on the search engine can overlook vast swaths of the web.
Additionally, Google results tend to favor the most search engine optimized websites. These pages, however, usually have limited value during investigations.
One alternative for OSINT research: Intelligence X.
Intelligence X differentiates itself from other search engines in a handful of ways.
Firstly, it indexes content from a wider variety of sources, such as the darkweb, WhoIs records, public data leaks, and document sharing platforms. Users can also search with specific selectors, such as URLs, IP addresses, and email addresses.
Additionally, Intelligence X also keeps an archive of results, similar to the Wayback Machine. But unlike other archival services, the site preserves all data sets no matter how controversial.
For example, Intelligence X has indexed footage from the 2021 Capitol Hill riots and Facebook’s data leak of 533 million profiles. The service has also archived data collected from email servers of well-known political figures like Donald Trump and Hillary Clinton.
For OSINT analysts and researchers, such information can be incredibly useful in a variety of circumstances.
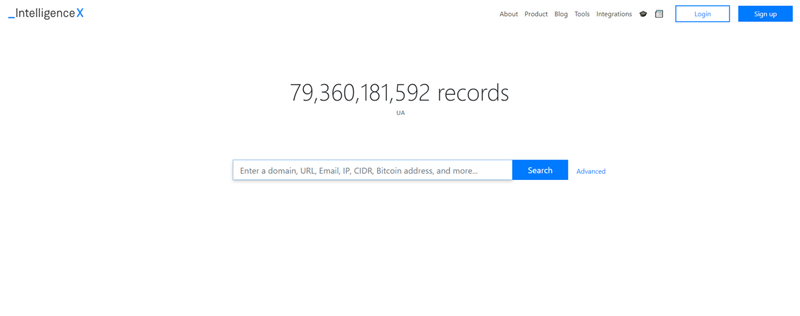 A screenshot of the Intelligence X search engine.
A screenshot of the Intelligence X search engine.
7. Exif Viewer
[Note: A previous version of this article included a link to Jeffey’s Metadata Viewer. This website has since gone offline, so we have updated this article to feature one of our favorite alternatives.]
Pictures posted online reveal a lot more than you might think.
When you take a photo, your smartphone or digital camera records a wealth of supplementary information about the image. These details, called EXIF data, include facts such as ISO speed, aperture, camera model, focal length, and white balance.
Such EXIF data can have enormous value during an OSINT investigation. And in most cases, researchers can access this information with the right tools.
One of our favorite free OSINT websites for doing this: Exif Viewer.
Jeffrey's Image Metadata Viewer is a browser-based tool that allows you to view EXIF data from uploaded photos. That usually includes file names, the type of camera used, the time and date the image was taken, as well as any embedded GPS coordinates.
This can have several applications for researchers.
For instance, individuals repurposing photographs to spread misinformation online usually don’t update an image’s EXIF data. So reviewing this information can often reveal a photo to be a fake.
Alternatively, GPS coordinates embedded in an image could reveal the location of an executive or VIP. Or it could reveal the location of a person of interest during an investigation.
A screenshot of ExifViewer.
OSINT Websites Won’t Overcome a Poor Methodology...
...but they will help you gather intelligence faster and more effectively.
Although you could list thousands of other OSINT websites and resources, the ones mentioned above highlight the best tools that every security team should bookmark.
Try them out and see how they enhance your intelligence operations.

